Lymphedema
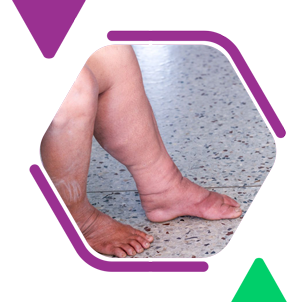
What is lymphedema?
Lymphedema is a chronic lymphatic condition that causes unsightly swelling in one or more body areas. It might be inherited (Primary Lymphedema) or it can develop as a result of surgery, illness, radiotherapy, or other physical stress (Secondary Lymphedema).
What Are The Causes ?
What Are The Types of ?
There are mainly two types :-
1) Primary
2) Secondary
1) Secondary :-
- Surgical damage
- Infection in lymphatic vessels
- Radiation therapy for cancer
- Cancer
2) Primary :-
Primary lymphedema develops when lymphedema occurs without any documented injury or illness.
- Onset at age 36 and older
- Onset after birth but before age 36
- Present at birth.
What is the most common symptom?
- Enlarged lymph nodes in your neck without pain
- Persistent fatigue.
- Fever.
- Night sweats.
- Shortness of breath.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Itchy skin.
What Is the most common treatment?
Therapy :-
Lymphedema treatments is determined by the degree and scope of the problem. Because there is no cure for lymphedema, prevention, and management of the condition are critical.
Some therapists recommend:-
- Wearing a customized bandage
- Regular arm pumping
- Eating a well-balanced diet
- Keeping the arm raised
- Infection Prevention
Surgery
Surgical surgery may be considered once edema has advanced to phases 3 or 4. surgery can entail a variety of procedures.: –
- Lymph node transplant
- Creation of new drainage paths
- Removal of fibrous tissue
- Liposuction
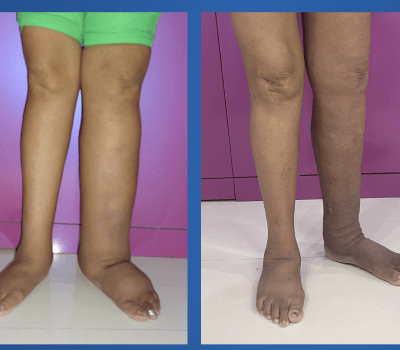
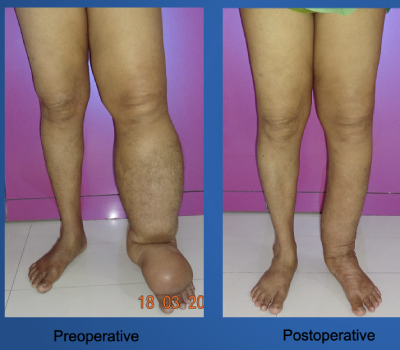
It a chronic condition characterized by the abnormal accumulation of lymph fluid, often manifests as unsightly swelling in various parts of the body. It can arise from a multitude of factors, ranging from genetic predisposition to secondary effects of surgeries, illnesses, or therapeutic interventions like radiation therapy. The lymphatic system, crucial for immune function and fluid balance in the body, becomes compromised when lymphatic channels are obstructed, leading to the buildup of lymph fluid beneath the skin.
Understanding Lymphedema
Anatomy of the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is a vital component of the body’s immune system, comprising a network of vessels and nodes that transport lymph—a clear fluid containing white blood cells—to filter out toxins, waste products, and pathogens. Lymph nodes, distributed throughout the body, act as filtration stations, removing harmful substances before the lymph rejoins the bloodstream.
Causes
Lymphedema may be classified into two main types: primary and secondary.
- Primary : It occurs without any identifiable injury or illness, often stemming from genetic abnormalities that affect the development or function of the lymphatic system. It may manifest at birth or later in life.
- Secondary : Secondary develops as a consequence of external factors that disrupt the normal functioning of the lymphatic system. Common causes include surgical interventions (such as lymph node removal during cancer surgery), infections affecting lymphatic vessels, radiation therapy for cancer treatment, or the presence of tumors that obstruct lymphatic flow.
Symptoms
The presentation of varies depending on its severity and the affected body part. Common symptoms include:
– Swelling in the arms, legs, or other regions
– Feeling of heaviness or tightness in the affected limb
– Restricted range of motion
– Discomfort or pain
– Skin changes, such as thickening or hardening
– Recurrent infections in the affected area
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis
Diagnosing typically involves a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and imaging studies such as lymphoscintigraphy or MRI to assess lymphatic flow and identify any blockages or abnormalities. Differential diagnosis may be necessary to rule out other conditions causing similar symptoms.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for , various treatment modalities aim to alleviate symptoms, manage swelling, and reduce the risk of complications. Treatment strategies may include:
- Compression Therapy: Wearing compression garments or bandages helps reduce swelling by providing external pressure to support lymphatic circulation.
- Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD): This specialized massage technique stimulates lymphatic flow, facilitating the drainage of excess fluid from affected areas.
- Exercise and Physical Therapy: Gentle exercises and movements can promote lymphatic drainage and improve muscle function, reducing the severity of swelling and enhancing mobility.
- Skin Care: Proper skincare practices, such as keeping the skin clean, moisturized, and protected from injury, help prevent infections and complications associated with lymphedema.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding activities that may exacerbate swelling, can contribute to overall management of the condition.
In cases where conservative measures are ineffective or the condition progresses to advanced stages, surgical interventions may be considered. Surgical options for lymphedema include:
– Lymphatic Microsurgery: Procedures such as lymph node transplantation or lymphovenous anastomosis aim to create alternative pathways for lymphatic drainage or restore damaged lymphatic vessels.
– Debulking Surgery: Surgical removal of excess tissue (such as fibrous deposits) or liposuction to reduce swelling and improve limb contour may be recommended in select cases.



 Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment