Gynecomastia is a medical condition characterized by the enlargement of male breast tissue. This condition, affecting up to 60% of males at some point in their lives, can lead to significant emotional distress. Men suffering from this surgery often feel self-conscious and may avoid activities that require them to remove their shirts in public, such as swimming or changing in locker rooms. This comprehensive guide will explore the causes, classifications, diagnosis, and treatment options for gynecomastia, with a particular focus on the surgical options available at Saundarya City in Nagpur.
Causes :
It is primarily caused by an imbalance between the hormones estrogen and testosterone. Estrogen, although commonly associated with female physiology, is also present in males but in much lower quantities. It plays a role in the development of breast tissue. Testosterone, the hormone responsible for male traits and reproductive activity, generally counteracts estrogen’s effects. When the balance between these hormones is disrupted, it can occur.
Excessive Levels of Estrogen
When the male body produces too much estrogen or has insufficient levels of testosterone (a condition known as hypogonadism), breast tissue may enlarge. This hormonal imbalance can occur naturally, particularly during puberty, when hormone levels fluctuate.
Natural Hormone Changes
Natural changes in hormone levels can also lead to gynecomastia. For example, during infancy, male babies may have enlarged breasts due to exposure to estrogen from their mothers. Similarly, hormone levels can change during aging, leading to gynecomastia in older men.
Medications and Their Side Effects
Certain medications can also cause this surgery. These include anabolic steroids, anti-androgens used to treat prostate cancer, some HIV medications, anti-anxiety drugs, tricyclic antidepressants, certain antibiotics, and chemotherapy drugs. These medications can disrupt the hormonal balance, leading to breast tissue enlargement.
Health Conditions
Various health conditions can contribute to gynecomastia, including:
– Hyperthyroidism: Excessive thyroid hormone can increase the levels of estrogen in the body.
– Kidney Failure: Can alter hormone levels.
– Liver Disease: Affects the body’s ability to metabolize hormones.
– Tumors: Tumors in the testicles, adrenal glands, or pituitary gland can affect hormone production.
– Malnutrition and Starvation: Can lower testosterone levels while maintaining estrogen production.
Street Drugs and Alcohol
Substance abuse, including alcohol, marijuana, heroin, and amphetamines, can also lead to this surgery.
Classifications
It can be classified based on the underlying cause and severity of the breast tissue enlargement.
Primary
Primary gynecomastia typically develops during puberty in boys aged 13 to 17 due to hormonal imbalances. This condition is characterized by an excess of estrogen over testosterone. In most cases, primary gynecomastia resolves on its own as hormone levels stabilize.
Secondary
Secondary gynecomastia can affect men of any age and is often linked to weight gain. This condition, also known as pseudo-gynecomastia, is characterized by the accumulation of excess fatty tissue in the breast area, rather than the development of glandular breast tissue.
Clinical Grading
It can also be graded based on the severity of breast tissue enlargement and the presence of excess skin:
– Grade 1: Small growth with no extra skin on the chest.
– Grade 2: Moderate growth without excess skin.
– Grade 3: Moderate growth with some excess skin.
– Grade 4: Significant enlargement with a substantial amount of excess skin.
Diagnosis of Gynecomastia
Diagnosing gynecomastia involves a thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider, which includes a review of symptoms, a physical examination, and a detailed health history. To confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions such as breast cancer, several tests may be recommended:
– Blood Tests: To evaluate hormone levels.
– Mammogram: To detect abnormal growths or changes in breast tissue.
– Ultrasound: To obtain detailed images of the breast tissue.
Treatment Options for Gynecomastia
The optimal treatment for gynecomastia depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In many cases, especially when the condition arises spontaneously during puberty, gynecomastia may resolve on its own without treatment. However, in cases where the condition is caused by an underlying health issue or results in significant emotional distress, medical or surgical intervention may be necessary.
Medical Treatment
If gynecomastia is caused by an underlying health condition, addressing that condition can often alleviate the breast tissue enlargement. For example, changing medications that cause gynecomastia or treating thyroid dysfunction can help. Hormone therapy to balance estrogen and testosterone levels may also be considered.
Surgical Treatment
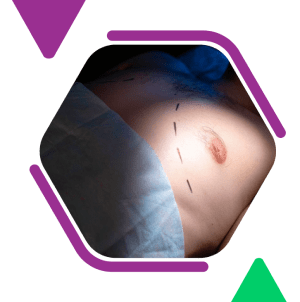
For persistent or severe cases of gynecomastia, surgery may be the most effective treatment option. The goal of gynecomastia surgery is to remove excess breast tissue and, if necessary, excess skin, to restore a more typical male chest contour.
Gynecomastia Surgery at Saundarya City
At Saundarya City in Nagpur, we offer advanced surgery performed by our expert surgeon, Dr. Suresh Chawre. The procedure involves the following steps:
– Anesthesia: Administered to ensure the patient is comfortable during the procedure.
– Incision: Made around the nipple or in the chest’s natural creases to minimize visible scarring.
– Tissue Removal: Excess glandular tissue, fat, and skin are removed. Liposuction may be used in conjunction with excision techniques to achieve the best results.
– Closure: The incisions are carefully closed to promote healing and reduce scarring.
Recovery After Surgery
Post-surgery, patients are advised to rest and avoid strenuous activities to allow the body to heal properly. Most patients can return to work within ten days, although this depends on the nature of their job. Common side effects such as swelling, bruising, pain, and numbness are usually temporary and subside within a few weeks. The surgical scar, typically around the nipple, is thin and blends in with the surrounding skin.
Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, this surgery carries potential risks and complications, including:
– Infection: Proper wound care and hygiene are crucial to prevent infection.
– Bleeding and Hematoma: Excessive bleeding or blood pooling under the skin may require additional treatment.
– Scarring: While efforts are made to minimize scarring, some degree of scarring is inevitable.
– Changes in Nipple Sensation: Temporary or permanent changes in sensation around the nipple may occur.
– Asymmetry: Although rare, there may be some asymmetry in the chest contour after surgery.
Psychological Impact and Support
Gynecomastia can have a profound psychological impact, leading to feelings of embarrassment, anxiety, and social withdrawal. Addressing the condition through surgery can significantly improve self-esteem and quality of life. However, it’s important for patients to have realistic expectations and to seek psychological support if needed. Counseling or therapy can help individuals cope with the emotional aspects of gynecomastia and the changes resulting from surgery.



 Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment