Blogs
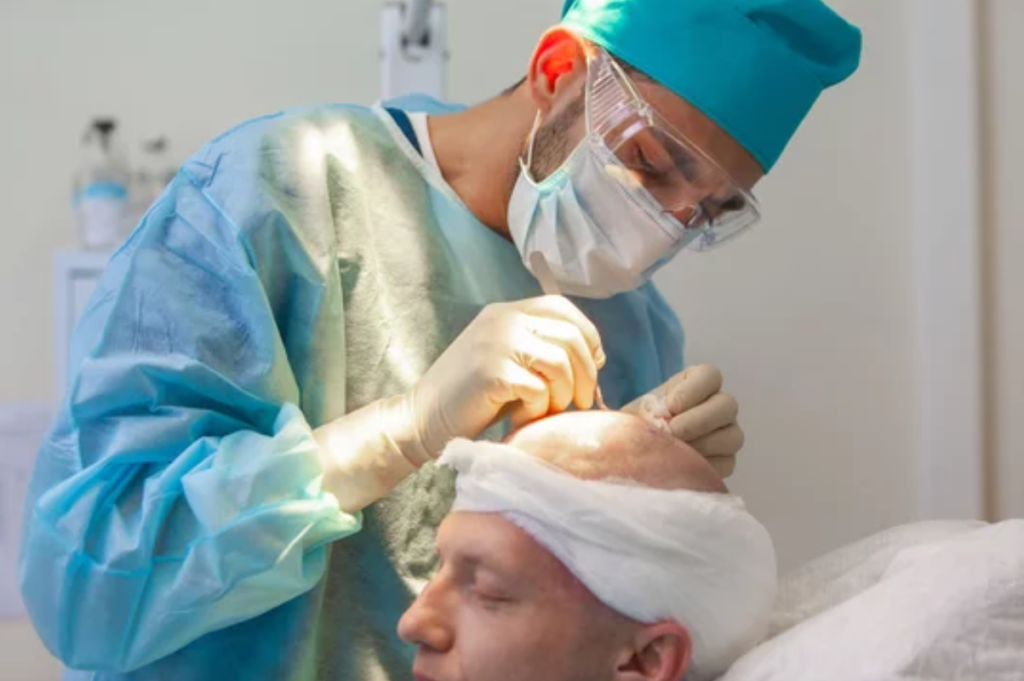
Complications of Hair Transplant: Understanding Risks and Managing Outcomes
Hair transplantation is a widely used technique for restoring hair, but like any surgical procedure, it comes with its own set of potential complications. Understanding these complications involves examining their origins, implications, and the interplay between various factors. Here’s a comprehensive guide to the common complications associated with hair transplants, their management, and what patients should know.
- Infection
Infection is a significant concern in hair transplant procedures due to the invasive nature of the surgery. The scalp becomes a potential site for bacterial, fungal, or viral infections due to numerous incisions made for graft insertion. The risk is influenced by the sterility of the surgical environment, the patient’s pre-existing health conditions, and post-operative care.
Management involves:
– Sterilization Protocols: Ensuring strict adherence to sterile techniques during surgery.
– Post-Operative Care: Educating patients on proper wound care and hygiene.
– Antibiotics: Administering antibiotics as needed if symptoms of infection arise.
- Bleeding
Bleeding can occur due to the disruption of blood vessels during the grafting process. While minor bleeding is normal, excessive bleeding can complicate the surgery and affect outcomes.
Management involves:
– Surgical Precision: Utilizing advanced techniques such as Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) to minimize bleeding.
– Hemostatic Agents: Applying agents to control bleeding.
– Monitoring: Regularly checking blood pressure and clotting status. In severe cases, additional interventions might be required.
- Swelling
Swelling or edema is a common response to surgical trauma, leading to puffiness around the forehead and eyes. It results from the body’s inflammatory response and fluid accumulation in tissues.
Management includes:
– Cold Compresses: Applying cold packs to reduce swelling.
– Head Elevation: Keeping the head elevated to minimize fluid buildup.
– Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Using prescribed medications to manage inflammation.
- Pain
Pain is a multifaceted issue influenced by physiological and psychological factors. It varies depending on the surgical approach and individual sensitivity.
Management involves:
– Analgesics: Using pre-operative and post-operative pain relief medications.
– Balancing Relief: Ensuring effective pain management while minimizing side effects.
- Scarring
Scarring results from the body’s healing process after surgery. The extent of scarring depends on the surgical technique and genetic predisposition.
Management includes:
– Advanced Techniques: Using methods like FUE to reduce scarring.
– Scar Treatments: Applying laser therapy or silicone gel to minimize prominent scars.
- Shock Loss
Shock Loss refers to the temporary loss of hair surrounding the transplanted grafts due to the trauma of the procedure. This is usually a temporary condition, with hair typically regrowing as the follicles recover.
Management involves:
– Supportive Care: Monitoring and managing patient expectations while ensuring normal hair growth cycle resumption.
- Graft Failure
Graft Failure occurs when transplanted hair follicles do not establish themselves successfully in the recipient area, leading to incomplete or uneven hair coverage.
Management includes:
– Meticulous Handling: Ensuring careful handling and optimal placement of grafts.
– Recipient Site Preparation: Ensuring proper blood supply and tissue quality for graft survival.
– Follow-Up Care: Monitoring and supporting follicle adaptation and growth.
- Uneven Hair Growth
Uneven Hair Growth can result from transplanted follicles growing at different rates or in inconsistent patterns.
Management includes:
– Additional Procedures: Performing touch-up sessions or extra transplants to achieve a uniform appearance.
- Itching and Discomfort
Itching and Discomfort are minor complications that occur as part of the healing process, often due to the inflammatory response and scab formation.
Management involves:
– Topical Treatments: Using prescribed treatments to alleviate itching.
– Avoiding Scratching: Following aftercare instructions to minimize irritation.
- Cyst Formation
Cyst Formation can occur due to blocked hair follicles or sebaceous glands, leading to discomfort or cosmetic concerns.
Management includes:
– Monitoring: Keeping an eye on cysts and addressing them if they become problematic.
– Minor Surgical Procedures: Removing or draining cysts if necessary.
- Poor Hair Growth
Poor Hair Growth is characterized by insufficient density or quality in the transplanted area.
Management involves:
– Further Evaluation: Assessing the transplant technique and considering additional treatments if needed.
- Asymmetry
Asymmetry occurs when the transplanted hair grows unevenly, affecting the hairline or overall coverage.
Management includes:
– Corrective Measures: Performing additional procedures to refine the hairline and achieve a balanced appearance.
- Allergic Reactions
Allergic Reactions to medications or materials used during or after the transplant can complicate recovery.
Management involves:
– Identifying Allergens: Adjusting medications or treatments based on identified allergies.
– Supportive Care: Providing care to mitigate reactions and ensure patient comfort.
- Numbness
Numbness in the scalp can result from nerve damage or irritation during the procedure, which can be temporary or, in rare cases, persistent.
Management involves:
– Monitoring Recovery: Observing the extent of numbness and providing supportive care.
– Nerve Healing: Ensuring proper care to facilitate nerve recovery and sensation restoration.
Hair transplant surgery, while effective for hair restoration, comes with potential complications that can impact outcomes and recovery. Understanding these complications and their management can help patients make informed decisions and prepare for a successful recovery. At Saundarya City, we prioritize comprehensive care and meticulous techniques to minimize complications and achieve the best possible results for our patients.
Popular Posts
Nose Surgery (Rhinoplasty)
Nose reshaping (rhinoplasty or a "nose job") is an operation to change the shape or size of the nose...
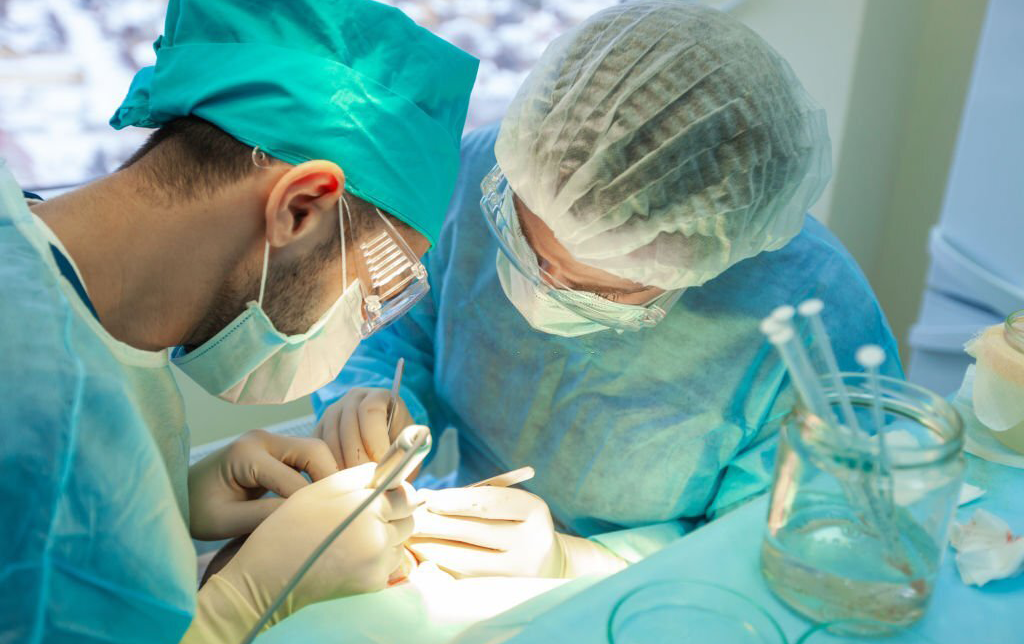
Best Hair Transplant Doctor In Nagpur Location
Saundarya City Uses Modern techniques have enabled advanced methods for surgical hair transplants that can help restore lost hair...



 Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment