Blogs
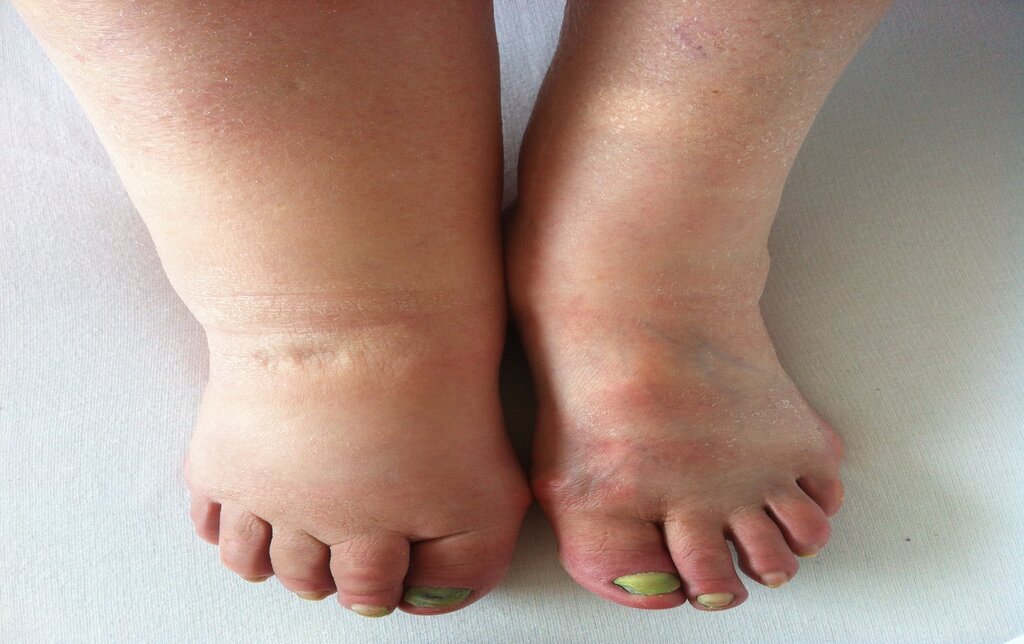
Understanding Lymphedema: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Lymphedema is a chronic condition characterized by the abnormal accumulation of lymph fluid, often resulting in noticeable swelling in one or more areas of the body. This condition can be both inherited or acquired due to various factors, and it can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding lymphedema involves exploring its causes, symptoms, types, and treatment options.
What Is Lymphedema?
Lymphedema occurs when the lymphatic system, which is crucial for fluid balance and immune function, becomes compromised. The lymphatic system is a network of vessels and nodes that transports lymph—a clear fluid containing white blood cells—to filter out toxins, waste products, and pathogens. When this system is obstructed, lymph fluid accumulates beneath the skin, leading to swelling.
Causes of Lymphedema
Lymphedema can be classified into two main types:
- Primary Lymphedema: This type occurs without any identifiable injury or illness and is often due to genetic abnormalities affecting the development or function of the lymphatic system. It can manifest at birth or later in life, typically in one of the following forms:
– Congenital Lymphedema: Present at birth.
– Early-Onset Lymphedema: Onset after birth but before age 36.
– Late-Onset Lymphedema: Onset at age 36 and older.
- Secondary Lymphedema: This type develops as a result of external factors that disrupt the normal functioning of the lymphatic system. Common causes include:
– Surgical Damage: Removal of lymph nodes or damage during surgery.
– Infection: Infections affecting the lymphatic vessels.
– Radiation Therapy: Used in cancer treatment, which can harm lymphatic tissues.
– Cancer: Tumors that obstruct lymphatic flow.
Common Symptoms of Lymphedema
Symptoms of lymphedema can vary based on the severity and affected areas but generally include:
– Swelling: In the arms, legs, or other body parts.
– Heaviness or Tightness: In the affected limb.
– Restricted Range of Motion: Difficulty moving the affected area.
– Discomfort or Pain: In the swollen regions.
– Skin Changes: Thickening or hardening of the skin.
– Recurrent Infections: In the affected area due to compromised immune function.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis: Diagnosing lymphedema involves a comprehensive approach, including:
– Medical History Review: Assessing symptoms and past medical conditions.
– Physical Examination: Observing swelling and other physical signs.
– Imaging Studies: Techniques such as lymphoscintigraphy or MRI to evaluate lymphatic flow and identify blockages.
Treatment Options: While there is no cure for lymphedema, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Compression Therapy: Utilizing compression garments or bandages to reduce swelling by applying external pressure to support lymphatic circulation.
- Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD): A specialized massage technique that stimulates lymphatic flow, helping to drain excess fluid from affected areas.
- Exercise and Physical Therapy: Gentle exercises and movements can enhance lymphatic drainage, improve muscle function, and reduce swelling.
- Skin Care* Maintaining clean, moisturized skin and protecting it from injury to prevent infections and complications.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding activities that may worsen swelling.
- Surgical Interventions: For advanced cases, surgical options may include:
– Lymphatic Microsurgery: Procedures like lymph node transplantation or lymphovenous anastomosis to create alternative drainage pathways or repair damaged vessels.
– Debulking Surgery: Removing excess tissue or performing liposuction to reduce swelling and improve limb contour.
Consult Saundarya City for Expert Care
If you or a loved one is struggling with lymphedema, Saundarya City offers specialized care and treatment options tailored to manage and alleviate symptoms. Our experienced team, led by Dr. Suresh Chawre, provides comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans to help you achieve the best possible outcomes.
Popular Posts
Nose Surgery (Rhinoplasty)
Nose reshaping (rhinoplasty or a "nose job") is an operation to change the shape or size of the nose...
Best Hair Transplant Doctor In Nagpur Location
Saundarya City Uses Modern techniques have enabled advanced methods for surgical hair transplants that can help restore lost hair...



 Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment